- Introduction
- Configuration settings for the LLP Listener
- Message encoding
- LLP delimiters
- Port
- Connection timeout
- IPv6 support
- Ack
- Use SSL
- Additional Information
- Port Management Tips
Introduction
An LLP Listener component listens on a specified port for HL7 messages using the LLP protocol.
Configuration settings for the LLP Listener [top]
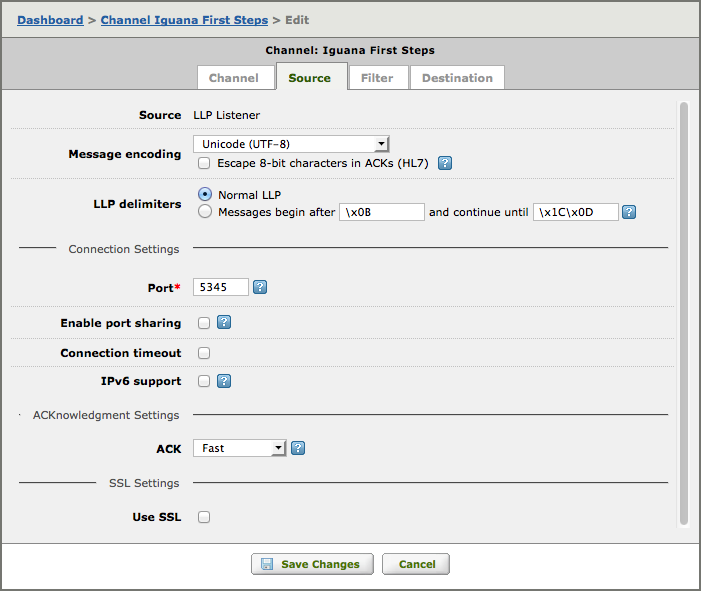
Message encoding: [top]
- From the Message encoding list box, select the encoding that incoming messages will use.
- Check Escape 8-bit characters in ACKs (HL7) if you want escape 8-bit characters in ACK messages.
If you choose to escape 8-bit characters you can (optionally) choose the escape character:
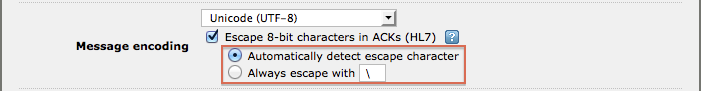
The Automatic setting will use the escape character specified in the MSH segment of the message (default = “\”).
LLP delimiters: [top]
- You can (optionally) choose custom LLP delimiters.

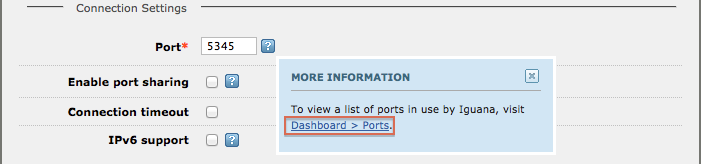
Port: [top]
- In the Port field, specify a port number to use.
- Check Enable port sharing to allow multiple LLP Listener components to use the same port.
By default, Iguana chooses a port number that is currently not in use. If you want to choose a port number manually you can check the used ports via the link in the help.
When Enable port sharing is selected, connections are limited to a Remote host and an optional Alternate host:
- Enter the host name or IP address for the Remote host that will be the source of incoming messages.
- Optionally enter the host name or IP address for an Alternate remote host.
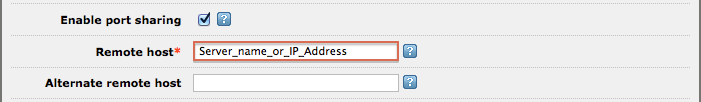
This allows multiple LLP channels to share the same port.
Connection timeout: [top]
- Check Connection timeout to allow connection timeouts.
- Enter the number of minutes to wait before timing out (default is 30minutes).

IPv6 support: [top]
- Check IPv6 support if this channel will connect to a client that uses an IPv6 Internet address.

If you do not see the checkbox, it means IPv6 support is not enabled on your server. In almost all cases IPv6 can be enabled.
If you are using IPv6 on Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, your channel will not be able to connect to an application that is using an IPv4 address. See this link for more information: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms738664%28VS.85%29.aspx.
Ack: [top]
- Select Fast to allow Iguana to generate ACKnowledgment messages.
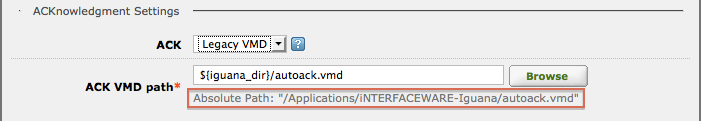
- Select Translator or Legacy VMD if you want to generate custom ACKnowledgment messages.
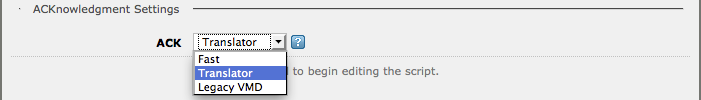
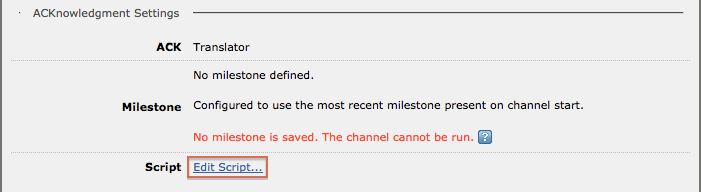
Choosing Translator adds a Script to the LLP Source for you to use to generate custom ACKs.
Choosing Legacy VMD uses the autoack.vmd by default – but you change it if you wish. You can use an absolute file path or a relative file path for the VMD file – the absolute path is displayed for confirmation.
Use SSL: [top]
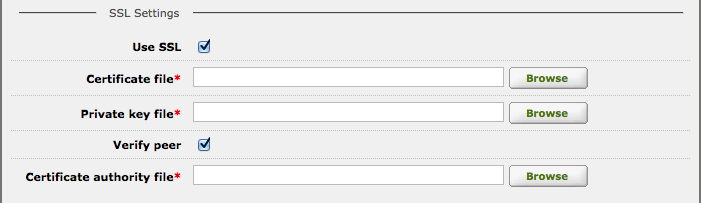
- Check Use SSL to receive messages securely using SSL (Secure Socket Layer).

Some additional fields will appear that you must fill out to specify the SSL connection:
- Enter the name of the Certificate file.
- Enter the name of the Private key file.
- Check Verify Peer to verify the server sending you messages.
- If you checked Verify Peer then enter the name of the Certificate authority file.
Tip: To create certificate files and private key files for testing see, see the FAQ: How to create self-certified SSL certificate and public/private key files.
Additional Information [top]
Port Management Tips [top]
When you create a new LLP listener channel in Iguana, you will need to supply a port number. This is a number between 1 and 65535 that identifies the TCP connection that an application such as Iguana uses to send or receive information. For example, port 80 is the standard connection used by your web browser to send and receive information to and from the Internet.
Note: For more information on TCP ports, which are also called Internet sockets, see the Wikipedia entry on TCP ports.
By default, when you create a new channel, Iguana will select a port that is not currently in use. However, you can specify any port you want.
Note: There is no standard HL7 port: in most health care environments, HL7 messages are transmitted, using the LLP protocol, through a number of different ports. Because there is no standard port, you can choose whatever port you like for your Iguana channel, provided it is not in use.
The following tips may help you manage your ports effectively:
- Be sure not to use a port that is likely to be used by other applications you are running. Even if such a port is not in use now, there are likely to be conflicts in the future. Examples of such ports include 443 (HTTPS), 1433 and 1434 (Microsoft SQL Server) and 3306 (MySQL). For a complete list of ports in common use, see this list of commonly used ports.
- If you are using a large number of channels or using a number of servers, choose a block of consecutive ports that is not in use on any of your servers. This will ensure that you can transfer channels to and from servers without creating any conflicts.
- If you are running a test Iguana server that duplicates the channels in your production environment, ensure that the LLP Listener source components and LLP Client destination components of your test server channels use different ports from those used in your production server. A port can only be used by one server at a time.
