Modules: Structure
Contents
We discuss three commonly used Lua module structures:
- Recommended best practice: Module with a local table interface with a
returnstatement at the end of the module, this is the method recommended by the Lua committee - Good: Module with a global table interface, this method has now been deprecated by the Lua committee
- Do not use: Use
module(...,package.seeall)syntax, this is an older method with definite disadvantages
1. Module with a local table interface
This is our recommended module structure.
The “advantage” of this method is that the module functions remain private (you cannot see them in the _G table). Many Lua developers prefer this since it gives tighter control over what symbols are global and which are not.
How it works:
- Module name not exposed globally
- The module uses a local table as the interface
- Insert all functions, variables etc that you wish to expose into the interface table
- The last line of code in the module returns the interface table
- Private functions are declared as local and placed at the top of the module
Example code:
Main:
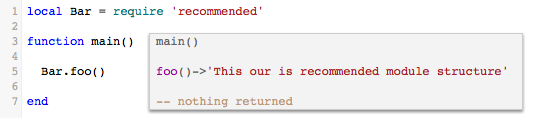
Note: this works because require() is actually just another Lua function (unlike the C/C++ #include statement, which is a preprocessor directive).
Module:

2. Module with a global table interface
This is also a good module structure, but the first method is preferred.
The “disadvantage” of this method is that the module functions are not private (you can see them in the _G table). If you prefer to make the module methods global then choose this method.
How it works:
- Module name exposed globally
- The module uses a global table as the interface
- Insert all functions, variables etc that you wish to expose into the interface table
- Private functions are declared as local and placed at the top of the module
Example code:
Main:
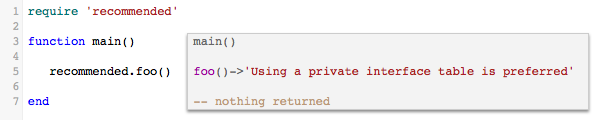
Module:
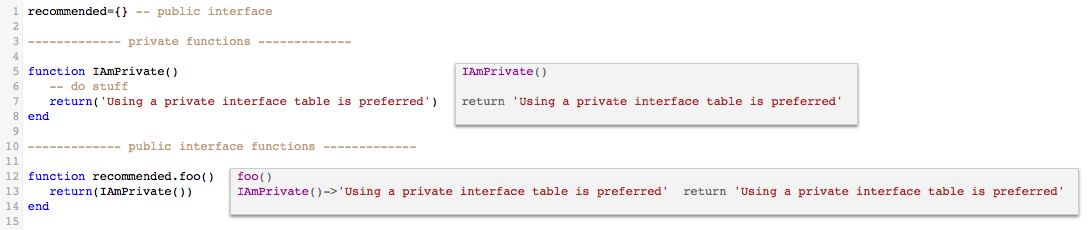
There are many ways to create modules in Lua, this method is simple and reasonably private. Even though this has been deprecated, we still think it is a reasonable compromise.
Many of the modules available on our wiki still use this syntax, they will eventually be changed to using private interface tables.
3. Using the module(...,package.seeall) syntax
Using module(…,package.seeall) syntax when defining modules produces interfaces which are not pleasant to use with auto-completion in the Translator. The problem with the module(…,package.seeall) is it pulls in all the global symbols from the _G table into the module table which makes for a lot of noise showing through when using autocompletion.
